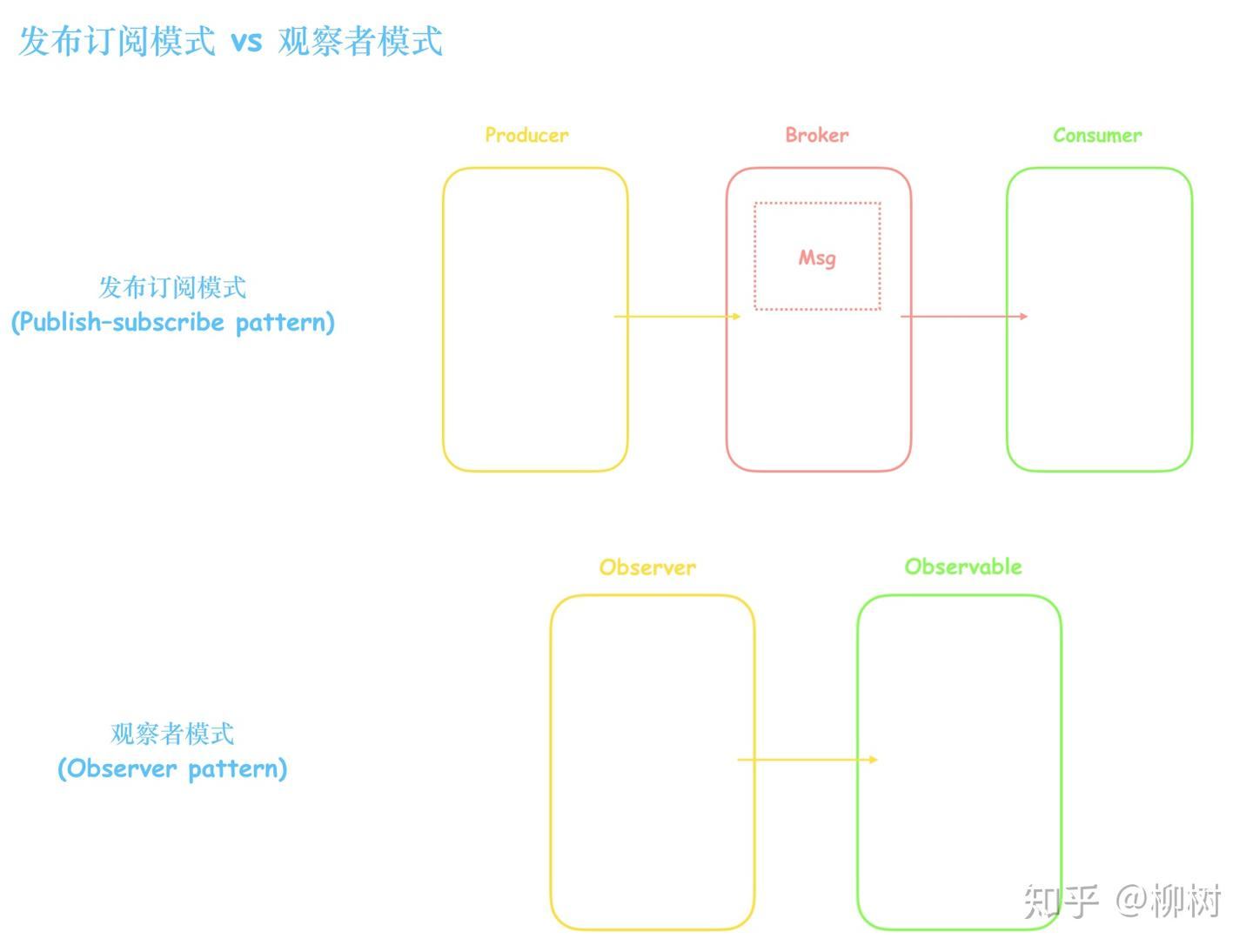
ref: 观察者模式 vs 发布订阅模式 - 知乎
观察者模式也是实现类似的功能,不过其是松耦合的,发布订阅模式中间加入了 Broker 作为中间件。
实现例子
ref: 理解【观察者模式】和【发布订阅】的区别观察者模式和发布订阅这两个东西听起来都不陌生,但是它们的差异究竟是什么,以及它们有 - 掘金
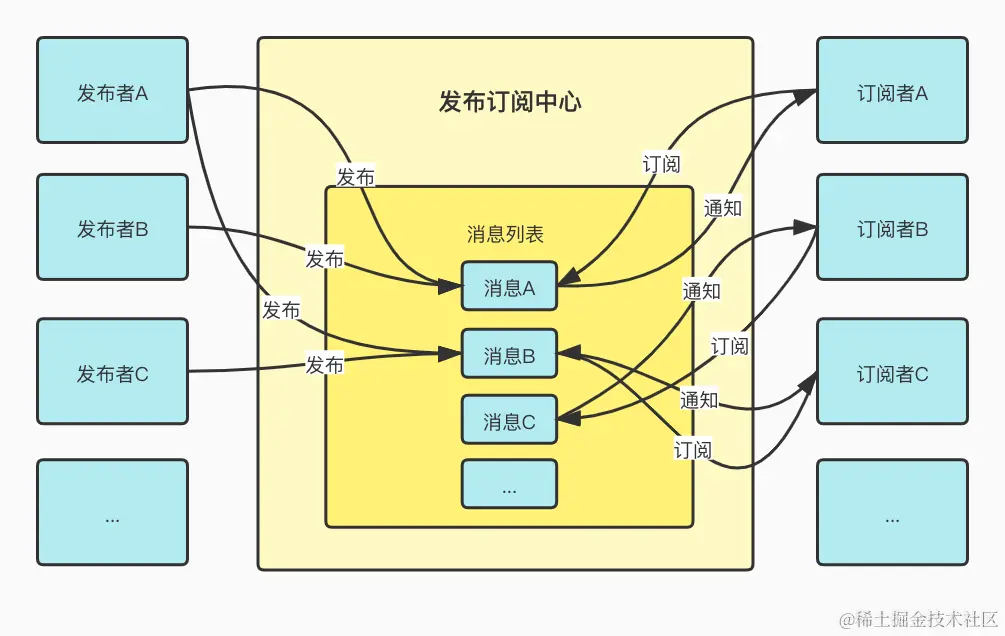
发布订阅中心
class PubSub {
constructor() {
this.messages = {};
this.listeners = {};
}
publish(type, content) {
const existContent = this.messages[type];
if (!existContent) {
this.messages[type] = [];
}
this.messages[type].push(content);
}
subscribe(type, cb) {
const existListener = this.listeners[type];
if (!existListener) {
this.listeners[type] = [];
}
this.listeners[type].push(cb);
}
notify(type) {
const messages = this.messages[type];
const subscribers = this.listeners[type] || [];
subscribers.forEach((cb) => cb(messages));
}
}- 保存数据结构 messages 和 listeners,messages 作为数据缓存,listeners 保存侦听对象
发布者
class Publisher {
constructor(name, context) {
this.name = name;
this.context = context;
}
publish(type, content) {
this.context.publish(type, content);
}
}订阅者
class Subscriber {
constructor(name, context) {
this.name = name;
this.context = context;
}
subscribe(type, cb) {
this.context.subscribe(type, cb);
}
}外部使用
const TYPE_A = 'music';
const TYPE_B = 'movie';
const TYPE_C = 'novel';
const pubsub = new PubSub();
const publisherA = new Publisher('publisherA', pubsub);
publisherA.publish(TYPE_A, 'we are young');
publisherA.publish(TYPE_B, 'the silicon valley');
const publisherB = new Publisher('publisherB', pubsub);
publisherB.publish(TYPE_A, 'stronger');
const publisherC = new Publisher('publisherC', pubsub);
publisherC.publish(TYPE_B, 'imitation game');
const subscriberA = new Subscriber('subscriberA', pubsub);
subscriberA.subscribe(TYPE_A, (res) => {
console.log('subscriberA received', res);
});
const subscriberB = new Subscriber('subscriberB', pubsub);
subscriberB.subscribe(TYPE_C, (res) => {
console.log('subscriberB received', res);
});
const subscriberC = new Subscriber('subscriberC', pubsub);
subscriberC.subscribe(TYPE_B, (res) => {
console.log('subscriberC received', res);
});
pubsub.notify(TYPE_A);
pubsub.notify(TYPE_B);
pubsub.notify(TYPE_C);